HEALTH – THYROID DISORDERS

Dr Sunil Kumar Kota
Posted; Odishabarta
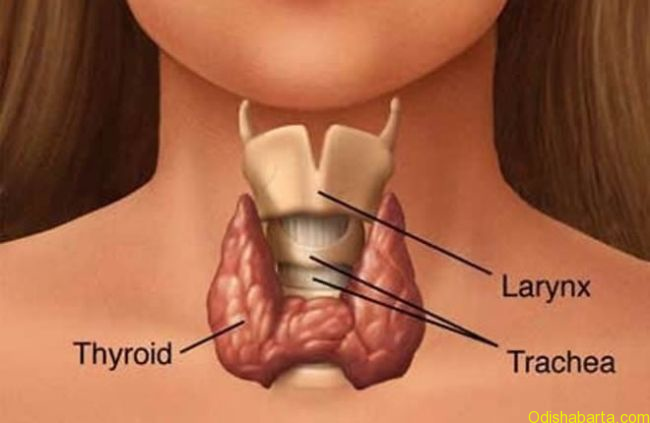
Thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland situated in front of the neck. It contains 2 lobes and is present underneath the voice box (Larynx). It releases 2 hormones, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxin (T4). Thyroid gland acts like a battery in our body (engine). These 2 hormones keep body and its organs active. They help in maintenance of proper growth. Another gland situated at the base of the brain called pituitary produces thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 & T4. In hypothyroidism (low levels thyroid hormones in the body), there is reduced release of T3 & T4. This inspires pituitary to produce more of TSH in order to further stimulate the thyroid gland. On the contrary, hyperthyroidism (low levels thyroid hormones in the body) leads to increased production of T3 & T4 with less TSH secretion from pituitary. So hypothyroidism is characterized by low T3, T4 with high TSH in blood.
WHAT CAUSES THYROID DISORDERS (?).
Iodine is necessary for functioning of thyroid gland. Therefore Iodine deficiency can hamper the functioning of the thyroid gland leading to decreased hormone production and release to blood. Now days, with increased usage of iodized salt, iodine deficiency are not the major cause for hypothyroidism.
Immune system is the defense mechanism in our body to protect us from various diseases. It acts through a special type of white blood cells, called as lymphocytes. Whenever there is an infection in our body, these lymphocytes produce antibodies which destroy the infectious agent like bacteria, virus etc. Sometimes disturbance in this immune system leads to production of auto antibodies, which attack our own body system like thyroid gland, pancreas, joint, hair root etc to give rise to thyroid disorders, diabetes, joint pain and hair loss etc.
In some children, thyroid gland is either absent or does not function properly, leading to congenital hypothyroidism from birth itself. In growing age, thyroid hormone is specifically important for both physical and mental growth. Immediate treatment is mandatory for this. Some persons have enlarged thyroid gland (goiter), nodular swelling or cancer. For all thyroid disorders together, the prevalence of 10%. Recent Indian studies have shown prevalence of 15-20% in general population. Thyroid problem is seen more commonly in ladies. This is because of effect of female hormone (estrogen) on immune system. Sometimes it appears first time during the pregnancy or sometimes after delivery of the child.
BENEFITS OF THYROID HORMONE:
1. T3 & T4 hormones keep every part of body active.
2. It provides energy to each and every part of our body
3. It activates the central nervous system
4. It promotes physical and mental growth in children.
5. It acts on almost all the systems of body like cardiovascular system, bones, blood producing bone marrow, reproductive system, gastrointestinal system.
SYMPTOMS OF HYPOTHYROIDISM:
– Excess dullness & Lethargy
-Dry skin with decreased sweating, hair loss
– Body swelling in hands, legs, face etc
-Cold intolerance (Feels colder than others)
– Sleepiness, tiredness, fatigability
-Depression
– Weight gain despite low appetite
-Memory loss
– Constipation
-Body aches & hoarse voice
(a) In elderly- Easy memory loss, less thinking capacity, weakness, depression. Highly uncontrolled state can give rise to coma.
(b) In children below 5 years- Laziness, Dull & idiotic look, poor physical and mental growth with delayed milestones and mental subnormality, constipation, hoarse cry, hair breakage, dry skin, enlarged tongue, prominence/ protuberance of umbilicus/ navel.
(c) In Older children- Apart from poor physical growth, poor performance in school, there can be delayed or early puberty/ sexual growth.
(d) In females- Excess bleeding, Irregular menses, decreased chances of fertility.
(e) In Pregnancy- Hypertension (High BP), Poor baby growth, premature delivery, low birth weight baby.
SYMPTOMS OF HYPERTHYROIDISM
– Weight loss despite increased appetite
-Wet skin with increased sweating, hair loss
– Trembling of hands
– Palpitation (↑ heart beat)
– Sleeplessness
– Heat intolerance (Feels more heat)
– Increased bowel movements
– Frequent menses, infertility
– Redness of eye
– Excess tearing from eyes
TREATMENT OF THYROID DISORDERS:
Hypothyroidism:Surgery is not required for treatment of hypothyroidism. I always tell my patients that hypothyroidism is not a disease, but a state of deficiency. So the doctor is trying to fill the void by replacing the deficit amount in form of a tablet. So thyroid tablet is not a medicine, rather a replacement. One tablet daily (dosage as decided by the doctor) has to be taken in empty stomach 1 hour before breakfast, even tea & coffee. Patients need to consult doctor once in 2-3 months initially. After thyroid levels are normalized, patients can consult once in 4-6 months. The goal of treatment is to maintain TSH in normal range (0.5- 5.0 mIU/ml)
Hyperthyroidism:Majority of patients are treated with oral medicines. Here follow up with doctor has to be done once in 2 months. Some patients need radio iodine therapy or surgery for uncontrolled disease or large goiter. The goal of treatment is to keep T4 in normal range (4.5-13 μg/dl).
Thyroid nodules:All thyroid nodules are to be evaluated by some blood tests, ultrasound of thyroid and a needle test (FNAC). Depending on the results, doctor would advise further management; either medical or surgical removal. Thyroid cancers are safest among all cancers. They don’t lead to death, or any other illnesses. After surgery, medical management and periodic blood test and thyroid scanning results in complete control of these cancers.
THYROID DISORDERS IN PREGNANT LADIES:
Thyroid disorders occur in increased frequency in pregnant females. The prevalence is estimated to be 20-22%. The female hormone (Estrogen) leads to increased production of Thyroid binding globulin/ TBG), which binds with T3 & T4. So these hormone levels are 1.5 times higher than that of nonpregnant females. Some patients develop thyroid problem for the first time during the pregnancy, where as in others a previously existing thyroid disorder gets
noticed first time during the pregnancy. Sometimes 3-6 months after delivery, thyroid problems may appear. Possibility is higher in ladies with family history of thyroid problems.
Hypothyroidism in pregnancy: If not adequately controlled, hypothyroid patients have lesser chances to conceive. Even after conceiving, chances of mental and physical sub normality are more. During first 3 months in the uterus (womb), baby does not have its thyroid gland and it depends on maternal thyroid hormone supply for its survival. So thyroid tablet should be taken immediately once hypothyroidism is diagnosed. A known hypothyroid lady getting pregnant should consult doctor immediately for possible enhancement of dose. After 3rd moth, baby develops its own thyroid gland. But the mother should continue taking the thyroid tablet. Till first 5 months, patients should consult doctor, once in every 4 weeks and then once in in 6-8 weeks. Patients’ thyroid hormone requirement gradually keeps increasing in order to supply the growing baby inside the uterus.
Uncontrolled hypothyroidism can lead to delivery of oversized baby, premature or early delivery, abortion, low birth weight and delivery of dead baby. Sometimes increase in BP, fits, kidney problem and increased amniotic fluid (cushioning fluid in the uterus) can also occur.
The goals for treatment differ from nonpregnant females. TSH targets are as below;
1st trimester: 0.1-2.5 mIU/ml
2nd trimester: 0.2-3.0 mIU/ml
3rd trimester: 0.3- 3.0 mIU/ml
Hypethyroidism in pregnancy:Chances of new onset hyperthyroidism are bit less in pregnancy. Sometimes, excessive vomiting in first 3 months and some placental tumors can also give rise to this type of picture (both clinical features and blood levels). In all the cases patients don’t need treatment. Based on some further tests your doctor would advise you accordingly.
If hyperthyroidism is not controlled properly, baby can develop goiter, excess bony maturation and growth retardation. Baby’s heart gates extra load with possible development of palpitation (increased heart rate) and heart failure. Baby too can develop hyperthyroidism. A known hyperthyroid lady getting pregnant should consult the doctor immediately for some change of medicines especially during first 3 months. Radioiodine therapy is contraindicated in pregnancy and lactation. Surgery if required has to be done after 3 months of pregnancy.
MYTHS & FACTS
T3, T4 & TSH are thyroid hormones.
Ans- No. T3 & T4 are thyroid gland hormones while TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) is produced by pituitary gland. As name TSH stimulates thyroid gland. TSH is more sensitive hormone for thyroid sufficiency than T3 & T4. Hence it is more used than T3 & T4 for diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid disorders. It has inverse relation with T3 & T4.
ALL HYPOTHYROIDISM PATIENTS WILL HAVE CLASSICAL SYMPTOMS OF HYPOTHYROIDISM.
Ans- No. Classical symptoms of hypothyroidism like puffiness of face, swelling all over the body, lethargy, dullness, weakness, muscle pain, leg cramps, dry and rough skin, excess hair fall, weight gain, menstrual problems etc are seen mainly with moderate to severe hypothyroidism (Serum/ Blood TSH more than 15 mIU/l).
HYOTHYROIDISM LEADS TO CONTINUOUS WEIGHT GAIN.
Ans- No. Moderate to severe hypothyroidism (Serum TSH more than 25 miu/l) is associated with moderate weight gain of 2-6 kgs. However after using thyroxine when serum TSH is stabilized hypothyroidism does not contribute to weight gain.
A LADY WITH THYROID CANNOT CONCEIVE:
Ans- No. On the contrarily hypothyroidism is the commonest treatable cause for female infertility. Chances of pregnancy increase several fold once hypothyroidism is corrected. Lady must continue thyroxine even during pregnancy. Thyroxine requirement often increase during pregnancy.
A LADY WITH HYPOTHYROIDISM GIVES BIRTH TO HYPOTHYROID BABY:
Ans- No. It generally does not happen. Baby can have increased risk of hypothyroidism in future due to genetic factors. But vertical transmission does not happen.
Once you get thyroid, it is forever:
Ans: By & large it is correct but not always true. Some of the hypothyroidism cases are reversible like borderline (sub clinical) hypothyroid cases, hypothyroidism during critical illness and drugs related hypothyroidism.
Thyroxin medicine can be taken anytime of the day.
Ans: No. Ideal time for thyroxine medicine is early morning, empty stomach. At least ½ hour – 1 hour gap should be given between medication and breakfast. More than ½ hour gap is alright. Some studies are there to show equal efficacy of thyroxine when taken bed time, 4 hours after dinner.
Thyroxin has lot of side effects:
Ans: No. Right dose of thyroxine is virtually free of side effects. Over dosage of thyroxine can cause hyperthyroidism like features e.g. palpitation, increased sweating, weight loss and irritability. Rapidly corrected hypothyroidism can sometimes precipitate heart pain in elderly people and increased intra cerebral pressure in children.
Thyroid medicines are risky during pregnancy:
Ans: No. Thyroid medicines are absolutely safe during pregnancy. In hypothyroid lady, thyroxine has several beneficial effects for mother as well as baby like reducing risk of abortion and other pregnancy related complication. It simultaneously improves IQ (intelligence) in baby.
THYROID SURGERY CAN CURE ANY THYROID DISORDER, INCLUDING HYPOTHYROIDISM:
Ans: No. Surgery is not required in hypothyroidism cases.
CHILDREN WITH THYROID DEFICIENCY CANNOT LIVE NORMAL ADULT LIFE:
Ans: No. With right dosage of thyroxine and regular treatment, children get normal height,pubertal development and normal future adult life.
CABBAGE AND CAULIFLOWER SHOULD NOT BE CONSUMED BY PATIENTS ON THYROXINE REPLACEMENT THERAPY:
Ans: No. These vegetables are thought to cause a decrease in hormone synthesis, especially in the backdrop of iodine deficiency. In the current scenario of iodized salt use, we don’t recommend to avoid them in patients who are on thyroxine hormone replacement therapy.
AUTHOR: Dr SUNIL KUMAR KOTA
MD (Med), DNB (Endocrinology), Consultant Endocrinologist,DIABETES & ENDOCARE Clinic, BERHAMPUR, ODISHA Email: [email protected] Phone: +917749804401






